Paying invoices can be a time-consuming task, especially for retailers who pay tens of thousands of invoices a month. Before payments are made, they need to check the goods have been received and the price and quantities on the invoice are accurate. The last thing they want is to be paying for things they shouldn’t be. But sometimes mistakes happen. They can be a result of human error like data entry mistakes. Or it could be something more sinister.
The accounts payable team usually compares the quantity and price on an invoice against the purchase order, as well as the stock that’s been received. Unfortunately, the more checks that are done, the more time consuming the process is. That’s where EDI can help.
What is two-way, three-way and four-way matching?
It’s where the accounts payable team checks the quantity and price of an invoice against what’s been ordered and agreed to, and what’s been received. The number of documents checked determines the type of matching (eg. two documents = two-way matching and so on).
So what documents are checked?[vc_column_inner width="2/6" css=".vc_custom_1593754872084{padding-top: 20px !important;padding-right: 0px !important;padding-bottom: 20px !important;padding-left: 0px !important;}"][vc_column_inner width="1/6" css=".vc_custom_1593753592414{padding-top: 20px !important;padding-right: 0px !important;padding-left: 0px !important;background-color: #1b75bb !important;}"]
Two-way matching
[vc_column_inner width="1/6" css=".vc_custom_1593753600250{padding-top: 20px !important;padding-right: 0px !important;padding-left: 0px !important;background-color: #1b75bb !important;}"]
Three-way matching
[vc_column_inner width="1/6" css=".vc_custom_1593753606451{padding-top: 20px !important;padding-right: 0px !important;padding-left: 0px !important;background-color: #1b75bb !important;}"]
Four-way matching
[vc_column_inner width="1/6"][vc_column_inner width="2/6"]
Purchase Order
(Check price and Qty)
[vc_column_inner width="1/6" css=".vc_custom_1593754902196{padding-top: 20px !important;background-color: #f9f9f9 !important;}"][vc_column_inner width="1/6" css=".vc_custom_1593754912282{padding-top: 20px !important;background-color: #f9f9f9 !important;}"][vc_column_inner width="1/6" css=".vc_custom_1593754919726{padding-top: 20px !important;background-color: #f9f9f9 !important;}"][vc_column_inner width="1/6"][vc_column_inner width="2/6"]
Order Acceptance/Response
(Check Qty)
[vc_column_inner width="1/6" css=".vc_custom_1593753317822{padding-top: 20px !important;background-color: #f9f9f9 !important;}"][vc_column_inner width="1/6" css=".vc_custom_1593753325484{padding-top: 20px !important;background-color: #f9f9f9 !important;}"][vc_column_inner width="1/6" css=".vc_custom_1593753338153{padding-top: 20px !important;background-color: #f9f9f9 !important;}"][vc_column_inner width="1/6"][vc_column_inner width="2/6"]
Order Receipts and Packaging Slips
(Check Qty)
[vc_column_inner width="1/6" css=".vc_custom_1593753317822{padding-top: 20px !important;background-color: #f9f9f9 !important;}"][vc_column_inner width="1/6" css=".vc_custom_1593753325484{padding-top: 20px !important;background-color: #f9f9f9 !important;}"][vc_column_inner width="1/6" css=".vc_custom_1593753338153{padding-top: 20px !important;background-color: #f9f9f9 !important;}"][vc_column_inner width="1/6"][vc_column_inner width="2/6"]
Invoice
(Check price and Qty)
[vc_column_inner width="1/6" css=".vc_custom_1593753317822{padding-top: 20px !important;background-color: #f9f9f9 !important;}"][vc_column_inner width="1/6" css=".vc_custom_1593753325484{padding-top: 20px !important;background-color: #f9f9f9 !important;}"][vc_column_inner width="1/6" css=".vc_custom_1593753338153{padding-top: 20px !important;background-color: #f9f9f9 !important;}"][vc_column_inner width="1/6"]And why do businesses choose to use two-, three- or four-way matching?
- It saves money
It helps businesses avoid overpaying for items, paying for duplicate items and paying for things they haven’t received.
- It safeguards the business
By checking the audit trail, it decreases the risk of paying fraudulent or incorrect invoices.
- It helps you pinpoint trouble suppliers
Verifying invoice amounts and price can help make sure your suppliers are not taking advantage of you. Suppliers who consistently make mistakes on invoices can cost your business and could be a sign to look for alternatives.
- Prepares businesses for audits
Auditors are specifically on the lookout for financial discrepancies. Compiling these documents in advance of an audit and checking that the numbers line up using the three-way matching process is a big step in the right direction.
How can EDI be used with two-, three- or four-way matching?
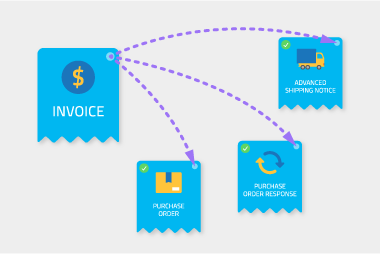
EDI (electronic data interchange) is the exchange of business information directly between business software. Think of a purchase order being created in one company’s accounting package, and it ‘magically’ appears in the supplier’s software; no email, no PDF, no manual data entry. Well, it’s not magic, it’s EDI!
So how does EDI work with verifying invoices? EDI gets all the data you need in your software – purchase orders, purchase order responses, shipping notices and invoices. It doesn’t require a person to type them in, they just appear. Once all the documents are received, a workflow can match each invoice with the corresponding purchase order, purchase order response and shipping documents. It’ll automatically check that the invoice price is what was agreed on, and the invoice quantity is not more than the amount of stock you received. It saves your accounts payable team time by automating the process.
The benefits of using EDI with two-, three- or four-way matching are:
- automated document matching
- reduced time to make payments
- reduced labour costs
- more time for your accounts payable team to work on value-adding tasks
- less human errors.
Implementing two-, three- or four-way matching
There are few things to think about before you start using two-, three- or four-way matching in your business.
Decide what you want to achieve
You can take verification to different levels of details, these could be:
- Making sure you’re not paying for more than you ordered
- Making sure you’ve received what you’re paying for
- Or something else.
This will determine what level of matching is best to achieve your goals.
Decide what messages and fields to match
Depending on what you want to achieve will determine what messages and data you’ll compare:
Two-way matching
You’ll probably match:
- the price in the purchase order (PO) with the price on the invoice and
- the quantity in the purchase order with the quantity on the invoice.
Three-way matching
In addition to the checks in two-way matching, you’ll probably match:
- the quantity of the goods shipped by the supplier.
This information can be found on the advanced shipping notice (ASN) or despatch advice.
Four-way matching
In addition to the checks in three-way matching, you’ll probably match:
- the quantity of the goods confirmed from your supplier. This information can be found in the purchase order response (POR), which you can ask your suppliers to send to you through EDI.
Decide what messages and fields to match
Once you know what messages you will be using you can get started with implementing EDI.
Working with an EDI provider
The first thing is choosing an EDI provider,
check out our blog to learn more about what to think about. After that, your EDI provider will build out your business rules to automate the checking of EDI messages. When your business rules are set to your requirements then you are able to go live.
Onboarding your suppliers
Suppliers can only start sending you messages (i.e. POs, invoices, ASNs and/or PORs) once you have onboarded them.
- Your EDI provider can easily connect to suppliers that already have EDI capability.
- For the suppliers who aren’t EDI compatible, it may be worth providing them with a portal option to start sending messages quickly and easily to you. For MessageXchange customers, we offer a free portal, Colladium, to help onboard suppliers.
If you’re interested in learning more about two-way, three-way or four-way matching, fill in the form below and one of our experts will get in touch.
Request a call
Chat with one of our experts
Just fill out your details below and we'll be in touch within one business day.