How eInvoicing works
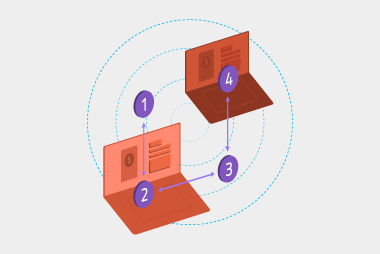
eInvoicing enables organisations to send and receive invoices electronically, directly to and from their software. It removes the need for unnecessary data entry and inaccurate OCR scanning. eInvoicing in Australia and New Zealand is provided through a network of interoperable Access Points, like MessageXchange, conforming to the Peppol standard that has been adopted around the world. More on that later. eInvoicing happens through a four-corner model, where corners one and four are the supplier and customer, and corners two and three are Access Points. Access Points connect to each other to exchange eInvoices. You can think of it like a telephone network – your phone and your friend’s phone are corners one and four, and your network provider (like Telstra, Optus or Vodafone) are corners two and three.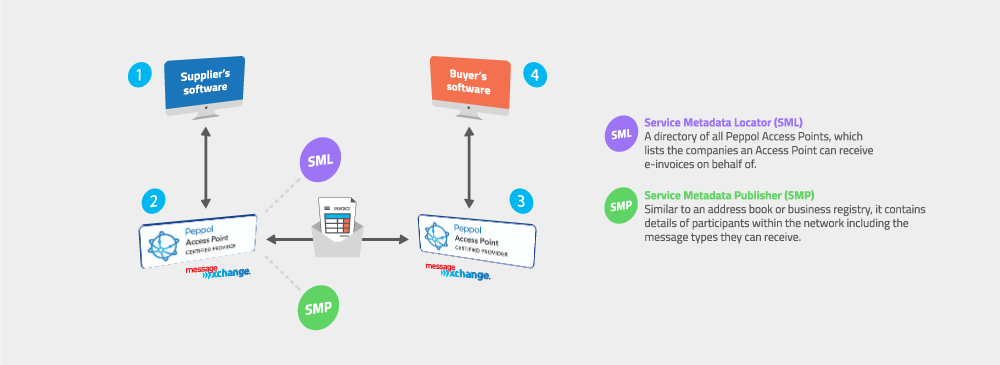
How eInvoicing works
There are a few different parties involved in eInvoicing in Australia and New Zealand, so it helps to know what each does.Peppol/OpenPeppol
Peppol is the international framework for eProcurement developed by a not-for-profit association, OpenPeppol. Think the four-corner model described above. The framework describes the file format that will be exchanged between Access Points (UBL) and the way that access points will connect to each other (AS4). It also outlines finer details, like how the SML and SMPs are used in the process. These are databases that are looked up to determine where to send the invoice to. The Peppol framework is used in Europe, North America and the Asia Pacific. In 2019, the Australian Government adopted the Peppol framework.Australian Taxation Office (ATO)
The ATO acts as the regulatory body responsible for overseeing the implementation and compliance of eInvoicing practices. The ATO has worked closely with industry stakeholders and government agencies to establish standards and guidelines for eInvoicing.Ministry of Business, Innovation and Employment (MBIE)
MBIE in New Zealand plays a significant role in promoting and facilitating the adoption of eInvoicing. MBIE is responsible for developing policies and regulations related to eInvoicing. It operates in a similar way to the ATO in Australia.Software providers
Software providers, in this case those who handle invoices, can develop and update their software to integrate with the Peppol network, enabling businesses to generate, send, and receive eInvoices seamlessly. These software providers often work in collaboration with the ATO and Access Points to ensure compliance and interoperability. Want to learn more about eInvoicing basics? Check out our whitepaper.Ready to implement eInvoicing in your business or want to learn more? Ask our experts by getting in touch below.Request a call
Chat with one of our experts
Just fill out your details below and we'll be in touch within one business day.