- receiving and stocking goods
- managing inventory
- managing of warehouse movements
- expediting shipments
- refund processing
- repackaging processes (co-packing).
An improved experience for your customers
We’ve seen 3PLs roll out EDI solutions, including portal solutions, for their customers. It makes the whole information flow between you, your customer and their customer easier. When your customer receives an order, they can accept it and at the same time, their EDI service can send a copy of it onto you so you know what to despatch, when and where. You can pick and pack the goods as usual, then when you create the shipping notice, you can send this via EDI to the recipient. Again, a copy can be sent to your customer for visibility. All of this ensures you’re not relying on PDFs and emails, and data is being exchanged in the quickest way possible.Benefits of EDI
Cost savings
With supply chain costs going up, now is the time for logistics companies to find ways to cut costs. During busy periods instead of receiving an email or phone call every time a customer needs stock shipped, you can get the request via EDI, straight into your software for processing. You won't have to worry about missing an email, or having staff on-hand to enter the PDF into your software and you won't need to 'scan' PDFs into your software and deal with potential scanning errors.Speed and accuracy
As your orders increase, your time to process them will only increase, unless you automate. EDI allows documents your customers need to be processed and sent faster. By reducing manual inputting, EDI also reduces the risk of inaccuracies in documents you send to your customers. Here are some stats that back the benefits:- can speed up your business cycles by 61%. Get documents directly into your software from your customers’ within minutes.
- It delivers at least a 30—40% reduction in errors.
Reduced manual processing
With staff shortages a big issue around the world right now, logistics companies need to find ways to make process more efficient. With EDI, not only does your speed improve, but the pressure on your staff is reduced. EDI makes it easier for you to process more shipments with fewer people which allows you to take on more customers and more of their orders.Compliance with retailers
If your customers supply to retailers, they’ll require documents via EDI. Send advanced shipping notices (ASNs) to the stock recipient, and even have a copy go to your customer for their visibility. Have more questions? Ask our experts by getting in touch below.Request a call
Chat with one of our experts
Just fill out your details below and we'll be in touch within one business day.



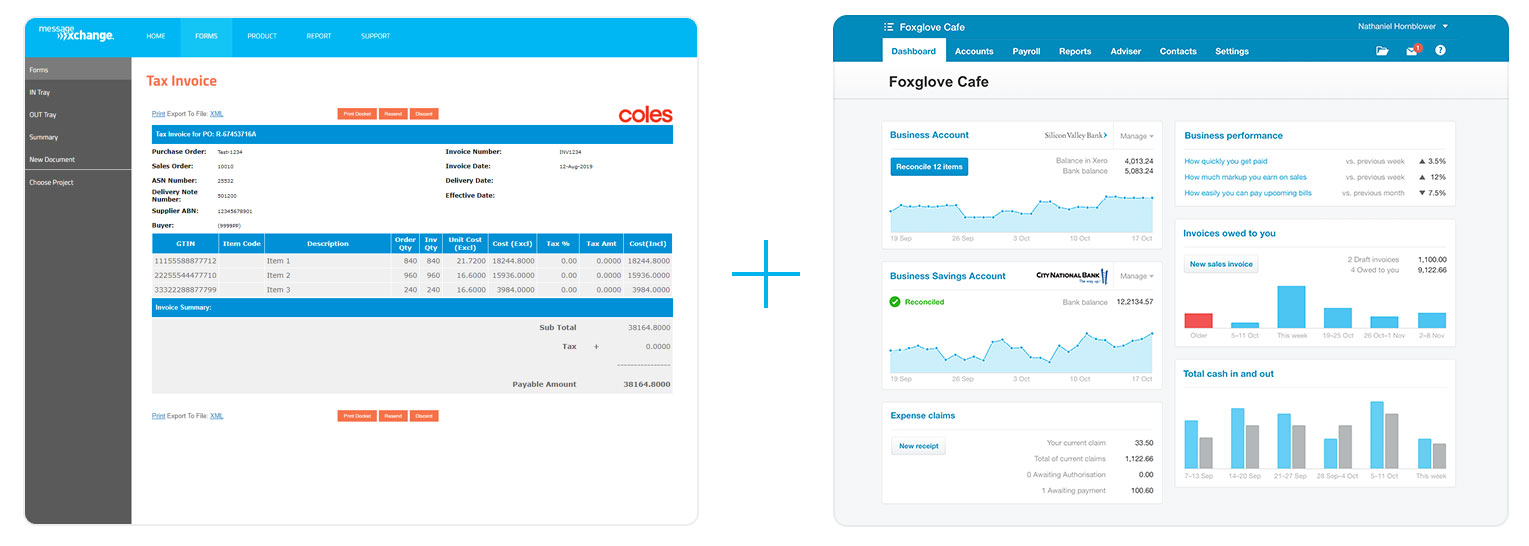 If you choose to go with our FormXchange product, you can even automate the process one step further. By turning on the integration between FormXchange and Xero, you can sync the invoices you enter in the EDI portal (FormXchange) directly to Xero, so your invoices are always up-to-date in your accounting software.
That means whenever you send an invoice to your customer on FormXchange, a copy will go to them, as well as to your Xero account. It’s that simple.
If you choose to go with our FormXchange product, you can even automate the process one step further. By turning on the integration between FormXchange and Xero, you can sync the invoices you enter in the EDI portal (FormXchange) directly to Xero, so your invoices are always up-to-date in your accounting software.
That means whenever you send an invoice to your customer on FormXchange, a copy will go to them, as well as to your Xero account. It’s that simple.